CNN
—
When US startup Make Sunsets released two weather balloons into the skies above Mexico’s Baja California peninsula last year, it kicked up a fierce debate about one of the world’s most controversial climate solutions.
The plan was for the balloons, filled with helium and a small amount of sulfur dioxide, to float high into the stratosphere. There they would burst, dispersing their load of sun-reflecting sulfur dioxide particles and cool the Earth, just a tiny bit.
Some dismissed it as a stunt. It is not clear if any particles were actually released or even if the balloons made it to the stratosphere. But Make Sunsets’ experiment is significant for crossing a threshold when it comes to a hotly-debated climate solution: solar geoengineering.
To its supporters, solar geoengineering is a fix we cannot ignore as the world hurtles toward climate disaster. For critics, it is a technology so dangerous we shouldn’t even research it.
The Next Big Idea: Reengineering the planet (2021)
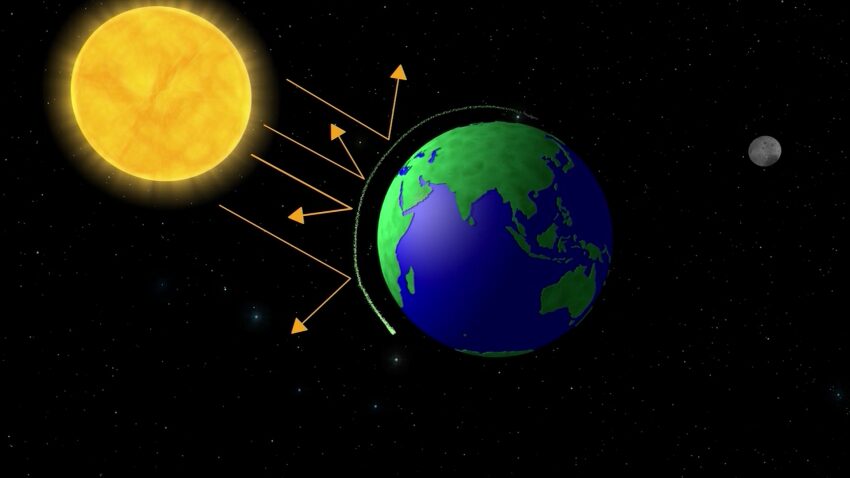
At its simplest, solar geoengineering, also known as solar radiation management, is an attempt to bring down the planet’s temperature by reflecting sunlight away or allowing more heat to escape into space.
There are three main techniques:
Marine cloud brightening involves trying to make the low clouds over the ocean more reflective by spraying them with sea salt.
Cirrus cloud thinning targets wispy clouds higher up in the atmosphere, seeding them with aerosol particles in an attempt to thin them, so they trap less heat.
The most-researched method, however, is stratospheric aerosol injection. It involves spraying aerosols – such as sulfur dioxide particles – into the stratosphere, more than 12 miles above the Earth’s surface, to reflect sunlight back into space. It could be done with balloons or specialized airplanes able to fly at high altitude.
The idea takes its cue from volcanoes. When Mount Pinatubo erupted in the Philippines in 1991, the sulfur dioxide it expelled high into the atmosphere had the effect of temporarily cooling the planet by 0.5 degrees Celsius (nearly 1 degree Fahrenheit).
The idea has been around since the 1960s, but it’s…
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at CNN.com – RSS Channel – HP Hero…