A giant impactor that severely dented Mars’ surface roughly 2.3 million years ago also carved out 2 billion smaller craters on the Red Planet as it shattered, a new study finds.
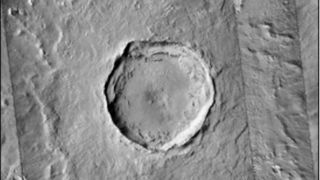
The main impact crater, known as Corinto, measures around 8.7 miles (14 kilometers) in diameter and is located in Elysium Planitia — a broad plain that straddles Mars‘ equator. Asteroids capable of leaving such a gigantic mark are estimated to only crash into the Martian surface every 3 million years or so, meaning Corinto may be the youngest crater of its size on the Red Planet, researchers revealed at the 55th annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference in Texas earlier this month.
“Corinto is a fresh impact crater in Elysium Panitia that produced one of the most extensive systems of…secondary craters on Mars,” the researchers wrote in a study released at the conference.
The team used data collected by the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) and the Context Camera (CTX) on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) to examine Corinto and its surroundings.
The object that formed Corinto pockmarked the surrounding landscape with smaller craters, as fragments splintered off and shot outward in ray-like patterns still visible today, according to the study. These secondary craters are concentrated in an area to the south and southwest of Corinto, with the farthest flung ejecta landing 1,150 miles (1,850 km) from the main crater.
The researchers grouped the secondary craters into four “facies,” based on their shape and distance from the main crater. Facies 0 craters, those closest to Corinto, appeared semicircular, whereas the farthest away, Facies 3 craters, were long and narrow.
“The observed differences…with distance from the crater likely result from variations in impact velocity and size of ejecta,” the researchers noted in the study.
The flight direction of the fragments that broke off the impactor, together with the slightly elliptical shape of the main crater, suggest the object came from the north and touched down on Mars at an oblique angle of 30 to 45 degrees, according to the study. The researchers also posit the object was made of “strong,…
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at Livescience…