MIT engineers have created more than 8,000 electric vehicle (EV) designs that can be combined with artificial intelligence (AI) to quickly build cars in the future.
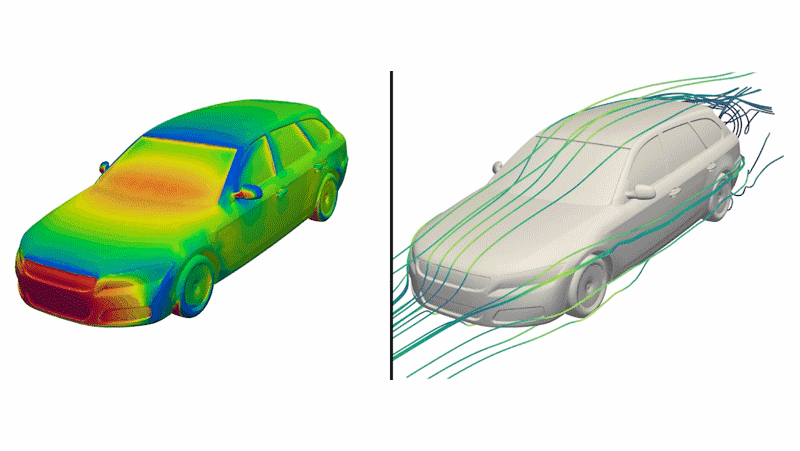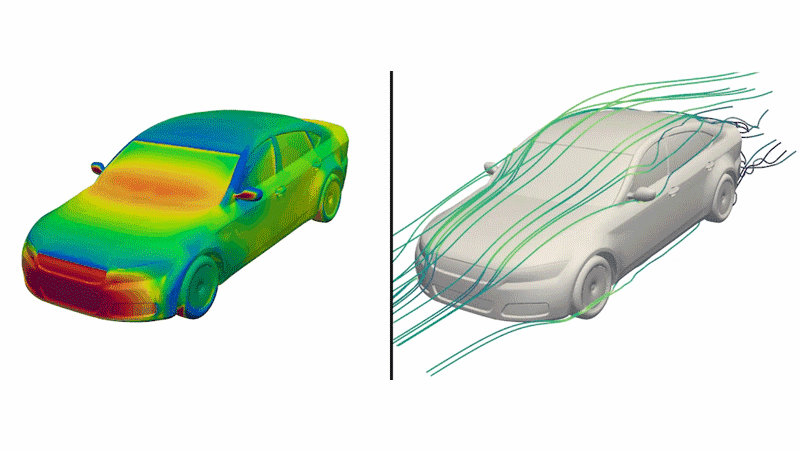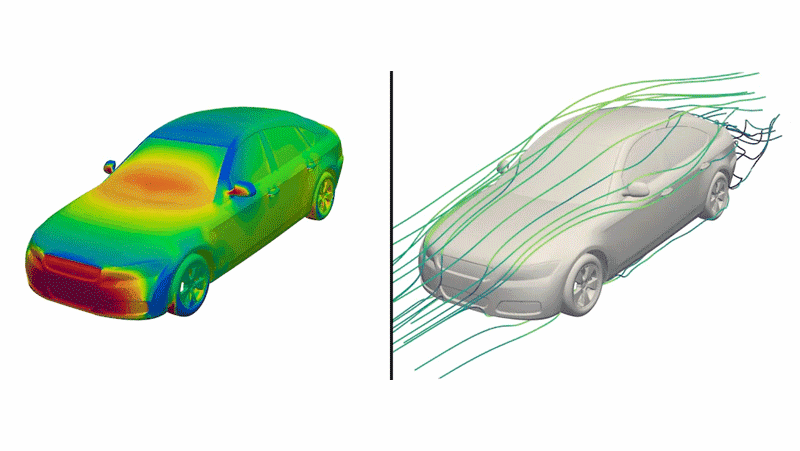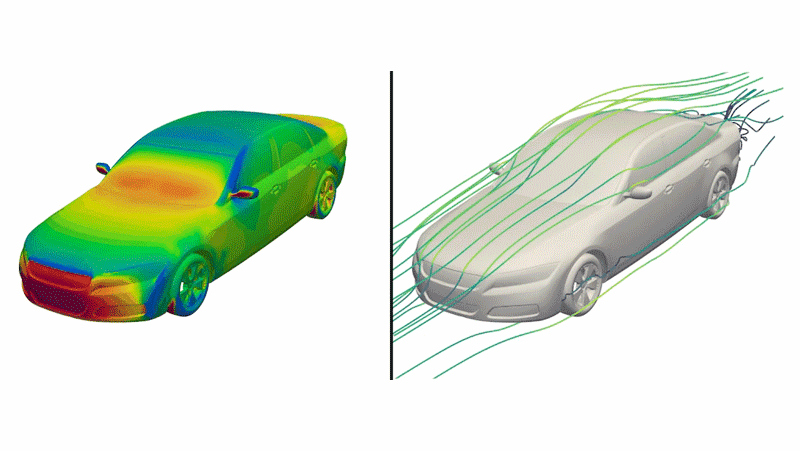
Dubbed “DrivAerNet++,” this open-source database includes designs that are based on the most common types of cars out right now, the engineers said, shown as 3D models that incorporate information such as how aerodynamic the design is.
Electric cars have been around for more than 100 years, but have skyrocketed in popularity recently. Designing these cars takes companies several years, resources, iterations and revisions until they reach a finalized design from which they can build a physical prototype.
Due to its proprietary nature, the specifications and results from these tests (as well as the aerodynamics of the prototypes) are private. This means significant advancements in EV range or fuel efficiency can be slow, the scientists said.
The new database, however, aims to speed up the search for better car designs exponentially.
This digital library of car designs include detailed data on specifications and aerodynamics. This digital library could be used to generate new electric car designs if combined with AI models in the future, the researchers said.
The engineers said that by streamlining a lengthy process, manufacturers can develop EV designs faster than ever before.
The team presented a paper, which was uploaded June 13 to the preprint arXiv database, outlining the dataset and how it can be combined with AI technologies. They described the work at the NeurIPS conference in Vancouver in December. a
Leaning on AI to create car designs in seconds
The dataset the researchers created produced 39 terabytes of data while consuming 3 million central processing unit hours with the MIT SuperCloud — a superpowerful cluster of computers used for scientific research that can be accessed remotely.
The team applied an algorithm that systematically tweaked 26 parameters, including vehicle length, underbody features, tread and wheel shapes, and windshield slope for each baseline car model. They also ran an algorithm that determined whether or not a newly generated design was a copy of something that already existed or genuinely new.
Each 3D design was then converted into different readable formats —…
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at Latest from Livescience…